รายชื่อแหล่งมรดกโลกที่กำลังตกอยู่ในภาวะอันตราย
หน้าตา
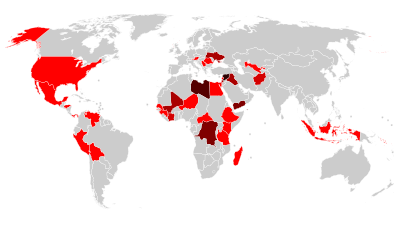
6 ที่หรือมากกว่า
5 ที่
4 ที่
3 ที่
2 ที่
1 ที่

- หมายเหตุ: ปีที่กล่าวถึงหลังแหล่งมรดกโลกนั้น ๆ คือปี พ.ศ. ที่ได้ขึ้นทะเบียนเป็นมรดกโลกที่กำลังตกอยู่ภาวะอันตราย
รายชื่อแหล่งมรดกโลกที่กำลังตกอยู่ในภาวะอันตราย ถูกรวบรวมโดยองค์การร่วมมือทางการศึกษา วิทยาศาสตร์ และวัฒนธรรมระหว่างประเทศ (ยูเนสโก) ผ่านทางคณะกรรมการมรดกโลก ตามอนุสัญญามรดกโลก มาตราที่ 11.4[nb 1] ซึ่งบัญญัติขึ้นเมื่อ พ.ศ. 2515 เพื่อกำหนดและจัดการแหล่งมรดกโลก
ข้อมูลเมื่อ กรกฎาคม 2019[update] มีแหล่งมรดกโลกที่กำลังตกอยู่ในภาวะอันตรายรวม 53 แห่ง (ธรรมชาติ 17 แห่ง, วัฒนธรรม 36 แห่ง) แบ่งตามภูมิภาคของยูเนสโกดังนี้: 21 แห่งอยู่ในรัฐอาหรับ (โดย 6 แห่งอยู่ในซีเรียและ 5 แห่งอยู่ในลิเบีย), 16 แห่งอยู่ในแอฟริกา (โดย 5 แห่งอยู่ในสาธารณรัฐประชาธิปไตยคองโก), 6 แห่งอยู่ในลาตินอเมริกาและแคริบเบียน, 6 แห่งอยู่ในเอเชียและแปซิฟิก และ 4 แห่งอยู่ในยุโรปและอเมริกาเหนือ แหล่งธรรมชาติที่ใกล้สูญพันธุ์ส่วนใหญ่ (12) อยู่ในทวีปแอฟริกา[1][2]
- *สำหรับชื่อแหล่งมรดกโลกในภาษาไทยนั้นได้แปลจากชื่อภาษาอังกฤษหรือฝรั่งเศสที่แต่ละแหล่งได้จดทะเบียนในบัญชีมรดกโลก
- Belize Barrier Reef System (2552)
- City of Potosí (2557)
- Humberstone and Santa Laura Saltpeter Works (2548)
- Mount Nimba Strict Nature Reserve (ร่วมกับประเทศกินี) (2524)
- อุทยานแห่งชาติวีเริงกา (2522)
- อุทยานแห่งชาติการองบา (2523)
- อุทยานแห่งชาติกาอูซี-บีกา (2523)
- อุทยานแห่งชาติซาลองกา (2527)
- เขตรักษาพันธุ์สัตว์ป่าโอกาปี (2539)
- อาบู เมนา (2544)
- Mount Nimba Strict Nature Reserve (ร่วมกันโกตดิวัวร์) (2535)
- Río Plátano Biosphere Reserve (2554)
- Tropical Rainforest Heritage of Sumatra (2554)
- อัสซูร์ (2546)
- นครโบราณซามาร์รา (2550)
- Hatra (2558)
- เยรูซาเลม (พ.ศ. 2525)
- งานแสดงสินค้านานาชาติเราะชีด กะรอมี ในตริโปลี (2566)
- Archaeological Site of Cyrene (2559)
- Archaeological Site of Leptis Magna (2559)
- Archaeological Site of Sabratha (2559)
- Old Town of Ghadamès (2559)
- Rock-Art Sites of Tadrart Acacus (2559)
- Rainforests of the Atsinanana (2553)
- Old Towns of Djenné (2559)
- ทิมบุกตู (2555)
- Tomb of Askia (2555)
- นันมาดอล : ศูนย์กลางพิธีการแห่งไมโครนีเชียตะวันออก (2559)
- Aïr and Ténéré Natural Reserves (2535)
- สถานที่พระเยซูประสูติ: โบสถ์พระคริสตสมภพและเส้นทางแสวงบุญ เบธเลเฮม (2555)
- ปาเลสไตน์ : ดินแดนแห่งมะกอกออลิฟและเหล้าองุ่น ภูมิทัศน์วัฒนธรรมทางทิศใต้ของเยรูซาเลม บะตีร (2557)
- เมืองเก่าเฮบรอน/อัลคาลิล (2560)
- อารามนักบุญฮิลาเรียน/ตัลล์อุมม์อามิร (2567)
- Fortifications on the Caribbean Side of Panama: Portobelo-San Lorenzo (2555)
- Chan Chan Archaeological Zone (2529)
- อนุสาวรีย์ยุคกลางในคอซอวอ (2549)
- เรนเนลล์ตะวันออก (2541)
- Ancient City of Aleppo (2556)
- Ancient City of Bosra (2556)
- Ancient City of Damascus (2556)
- Ancient Villages of Northern Syria (2556)
- Crac des Chevaliers and Qal’at Salah El-Din (2556)
- Site of Palmyra (2556)
- ศูนย์กลางประวัติศาสตร์ออแดซา (2566)
- เคียฟ : อาสนวิหารนักบุญโซเฟียและสิ่งปลูกสร้างอารามที่เกี่ยวข้อง และกือแยวอ-แปแชร์สกาลาวรา (2566)
- ลวิว กลุ่มศูนย์กลางประวัติศาสตร์ (2566)
- Selous Game Reservei (2557)
- Everglades National Park (2553)
- Historic Centre of Shakhrisyabz (2559)
- โกโรและท่าเรือ (2548)
- เมืองประวัติศาสตร์ซาบิด (2543)
- Old City of Sana'a (2558)
- Old Walled City of Shibam (2558)
- ที่หมายเด่นแห่งอาณาจักรซะบะอ์โบราณในมะอ์ริบ (2566)
อดีตแหล่งมรดกโลกในภาวะอันตราย
[แก้] รายการที่ถูกเพิกถอนจากบัญชีมรดกโลก
รายการที่ถูกเพิกถอนจากบัญชีมรดกโลกบางส่วน
| รายการ | ภาพ | ที่ตั้ง | เกณฑ์ | พื้นที่ ha (acre) |
ปีขึ้นทะเบียน มรดกโลก |
ปีที่ตกอยู่ใน ภาวะอันตราย |
เหตุผล | อ้างอิง |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| พื้นที่อนุรักษ์อึงโกรองโกโร | 
|
Arusha Region, 3°11′S 35°32′E / 3.183°S 35.533°E |
ธรรมชาติ: (iv), (vii), (viii), (ix), (x) |
—
|
1979 | 1984–1989 | สถานะการอนุรักษ์ที่ลดลง | [3][4] [5] |
| อุทยานแห่งชาติทะเลสาบพลิตวิตเซ | 
|
Lika-Senj County, 44°53′N 15°37′E / 44.883°N 15.617°E |
ธรรมชาติ: (vii), (viii), (ix) |
19,200 (47,000) | 1979 | 1992–1997 | ภัยคุกคามที่อาจเกิดขึ้นจากสงครามประกาศอิสรภาพโครเอเชีย | [6][7] [8] |
| นครเก่าดูบรอฟนีก | 
|
ดูบรอฟนีก-เนเร็ตวา, 42°38′25″N 18°06′30″E / 42.64028°N 18.10833°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (i), (iii), (iv) |
97 (240) | 1979 | 1991–1998 | สงครามประกาศอิสรภาพโครเอเชีย | [9][10] [11] |
| เหมืองเกลือหลวงวีแยลิตชกาและบอคญา | 
|
จังหวัดมาวอปอลสกา, 49°58′45″N 20°03′50″E / 49.97917°N 20.06389°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (iv) |
969 (2,390) | 1978 | 1989–1998 | ปัญหาความชื้น | [5][12] [13] |
| อุทยานแห่งชาติอีกวาซู | 
|
รัฐปารานา, 25°41′S 54°26′W / 25.683°S 54.433°W |
ธรรมชาติ: (vii), (x) |
170,086 (420,290) | 1986 | 1999–2001 | ถนนที่มีการเปิดอย่างผิดกฎหมายผ่านอุทยาน เขื่อนบนแม่น้ำอีกวาซู และการบินด้วยเฮลิคอปเตอร์ | [14][15] [16] |
| ภูมิภาคธรรมชาติและประวัติศาสตร์เชิงวัฒนธรรมแห่งกอตอร์ | 
|
Bay of Kotor, Kotor and surrounding territory, 42°29′N 18°42′E / 42.483°N 18.700°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (i), (ii), (iii), (iv) |
—
|
1979 | 1979–2003 | ความเสียหายหลังแผ่นดินไหวตั้งแต่วันที่ 15 เมษายน 2522 | [17][18] [19] |
| อุทยานแห่งชาติเยลโลว์สโตน | ไวโอมิง มอนแทนา และไอดาโฮ, 44°30′N 110°50′W / 44.500°N 110.833°W |
ธรรมชาติ: (vii), (viii), (ix), (x) |
898,349 (2,219,870) | 1978 | 1995–2003 | ตรวจพบอันตรายต่อปลาเทราต์เยลโลว์สโตน ตลอดจนการรั่วไหลของสิ่งปฏิกูลและการปนเปื้อนของเสียในบางส่วนของอุทยาน ภัยคุกคามที่อาจเกิดขึ้นต่อปริมาณและคุณภาพน้ำ กิจกรรมการขุดในอดีตและที่เสนอ โครงการควบคุมเพื่อกำจัดโรคบรูเซลโลซิสในฝูงกระทิงอเมริกัน | [20][21] [22] | |
| เขตสงวนธรรมชาติสแรเบอร์นา | 
|
Srebarna, Silistra Province, 44°06′50″N 27°04′40″E / 44.11389°N 27.07778°E |
ธรรมชาติ: (x) |
638 (1,580) | 1983 | 1992–2003 | การป้องกันน้ำท่วมตามฤดูกาลและการใช้ทางการเกษตรทำให้ปริมาณน้ำและนกลดลงหรือหายไป | [23][24] [25] |
| อังกอร์ | 
|
จังหวัดเสียมราฐ, 13°26′N 103°50′E / 13.433°N 103.833°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (i), (ii), (iii), (iv) |
—
|
1992 | 1992–2004 | [26][27] [28] | |
| ป้อมบะฮ์ลาอ์ | 
|
บะฮ์ลาอ์, 22°58′N 57°18′E / 22.967°N 57.300°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (iv) |
—
|
1987 | 1988–2004 | ความเสื่อมโทรมของโครงสร้างดินของป้อมและโอเอซิสแห่งบะฮ์ลาอ์ | [29][30] [31][32] |
| อุทยานแห่งชาติทิวเขารูเวนโซรี | 
|
Bundibugyo, Kabarole and Kasese District, 0°13′N 29°55′E / 0.217°N 29.917°E |
ธรรมชาติ: (vii), (ix) |
99,600 (246,000) | 1994 | 1999–2004 | สถานการณ์ความมั่นคงและขาดการเฝ้าติดตามพื้นที่สำคัญของอุทยาน | [14][33] [34] |
| บูทรินต์ | 
|
Sarandë District, 39°45′N 20°1′E / 39.750°N 20.017°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (iii) |
3,980 (9,800) | 1992 | 1997–2005 | ความเสียหายอันเนื่องมาจากการจัดการและการอนุรักษ์ | [35][36] [37] |
| ทิมบักตู | 
|
Circle and Region of Tombouctou, 16°46′24″N 2°59′58″W / 16.77333°N 2.99944°W |
วัฒนธรรม: (ii), (iv), (v) |
—
|
1988 | 1990–2005 | ภัยคุกคามจากการขยายตัวของทะเลทราย | [38][39] [40] |
| อุทยานแห่งชาติซังไก | 
|
Chimborazo, Morona-Santiago and Tungurahua Province, 1°50′S 78°20′W / 1.833°S 78.333°W |
ธรรมชาติ: (vii), (viii), (ix), (x) |
271,925 (671,940) | 1983 | 1992–2005 | การลักลอบล่าสัตว์อย่างหนัก การเลี้ยงปศุสัตว์อย่างผิดกฎหมาย การบุกรุก และภัยคุกคามที่อาจเกิดขึ้นจากโครงการก่อสร้างถนน | [41][42] [43] |
| อาสนวิหารโคโลญ | รัฐนอร์ทไรน์-เว็สท์ฟาเลิน, 50°56′29″N 6°57′29″E / 50.94139°N 6.95806°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (i), (ii), (iv) |
—
|
1996 | 2004–2006 | โครงการก่อสร้างอาคารสูงใกล้มหาวิหารอาจก่อให้เกิดความเสียหายต่อความสมบูรณ์ของทรัพย์สิน [nb 2] เพิกถอนสถานะอันตรายภายหลังการก่อสร้างอาคารถูกระงับและมีการเสนอพื้นที่กันชน | [44][45] [46] | |
| เขตรักษาพันธุ์นกแห่งชาติจูจ | 
|
Biffeche, 16°30′N 16°10′W / 16.500°N 16.167°W |
ธรรมชาติ: (vii), (x) |
16,000 (40,000) | 1981 | 1984–1988, 2000–2006 | ภัยคุกคามระยะยาวจากแผนการก่อสร้างเขื่อนท้ายน้ำ (พ.ศ. 2527); delisted[nb 2] (1988) เนื่องจากน้ำประปาเข้าอุทยานได้รับการประกันโดยการก่อสร้างประตูน้ำและกำลังเตรียมแผนการจัดการ ขึ้นใหม่[nb 3] (2000) เนื่องจากภัยคุกคามด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมและเศรษฐกิจที่เกิดจากสายพันธุ์ Salvinia molesta และ Pistia stratiotes ที่นำเข้ามา รวมถึงปัญหาเกี่ยวกับการจัดการน้ำในอุทยาน | [47][48] [49][50] [51][52] |
| กลุ่มโบราณสถานแห่งหัมปี | รัฐกรณาฏกะ, 15°20′6″N 76°27′43″E / 15.33500°N 76.46194°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (i), (iii), (iv) |
—
|
1986 | 1999–2006 | การก่อสร้างสะพานแขวนเคเบิล 2 สะพานบางส่วนภายในพื้นที่ทางโบราณคดีที่ได้รับการคุ้มครองในเมือง ซึ่งคุกคามความสมบูรณ์และความถูกต้องของสถานที่ | [53][54] [55] | |
| อุทยานแห่งชาติอิชเกิล | 
|
Bizerta, 37°10′N 9°40′E / 37.167°N 9.667°E |
ธรรมชาติ: (x) |
12,600 (31,000) | 1980 | 1996–2006 | การสร้างเขื่อนจำกัดการไหลของน้ำจืดลงสู่พื้นที่ ส่งผลให้ทะเลสาบและหนองน้ำมีความเค็มเพิ่มขึ้น รวมถึงจำนวนนกอพยพที่ลดลง | [56][57] [58] |
| ตีปาซา | 
|
Tipaza Province, 36°35′39″N 2°26′36″E / 36.59417°N 2.44333°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (iii), (iv) |
52 (130) | 1982 | 2002–2006 | การบำรุงรักษาที่ไม่เพียงพอส่งผลต่อความสมบูรณ์ของเขตและพื้นที่กันชน | [59][60] [61] |
| หุบเขากาฐมาณฑุ | 
|
27°42′14″N 85°18′31″E / 27.70389°N 85.30861°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (iii), (iv), (vi) |
167 (410) | 1979 | 2003–2007 | การสูญเสียองค์ประกอบดั้งเดิมบางส่วนหรืออย่างมากของเขตอนุรักษ์หกในเจ็ดเขต ส่งผลให้สูญเสียความถูกต้องและความสมบูรณ์ของทรัพย์สินทั้งหมดโดยทั่วไป | [62][63] [64] |
| พระราชวังแห่งอาบอแม | 
|
Zou Department, 7°11′26″N 1°59′36″E / 7.19056°N 1.99333°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (iii), (iv) |
48 (120) | 1985 | 1985–2007 | เสื่อมสภาพโดยทั่วไปเนื่องจากองค์ประกอบและการบูรณะที่ไม่เหมาะสมซึ่งแย้งกับความเป็นของจริงของสถานที่ | [65][66] [67][68] |
| ลุ่มน้ำเอ็ลเบอในเดรสเดิน | 
|
รัฐซัคเซิน, 51°3′N 13°49′E / 51.050°N 13.817°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (ii), (iii), (iv), (v) |
1,930 (4,800) | 2004 | 2006–2009 | การก่อสร้างสะพานวัลท์ชเลิสเชิน; ถูกเพิกถอนจากบัญชีมรดกโลกในปี 2552 หลังจากเริ่มก่อสร้างเมื่อปลายปี 2550 | [69][70] |
| นครที่มีป้อมปราการแห่งบากู พร้อมด้วยพระราชวังของชีร์วานชาฮ์และหอคอยหญิงสาว |

|
บากู, 40°21′59″N 49°50′7″E / 40.36639°N 49.83528°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (iv) |
—
|
2000 | 2003–2009 | ความเสียหายที่เกิดขึ้นระหว่างแผ่นดินไหวบากู พ.ศ. 2543 การพัฒนาเมือง และความพยายามในการอนุรักษ์ที่ไม่เพียงพอ | [71] |
| หมู่เกาะกาลาปาโกส | 
|
จังหวัดกาลาปาโกส, 0°40′S 90°30′W / 0.667°S 90.500°W |
ธรรมชาติ: (vii), (viii), (ix), (x) |
14,066,514 (34,759,110) | 1978 | 2007–2010 | ภัยคุกคามต่างๆ รวมถึงการป้องกันความเป็นไปได้ไม่เพียงพอสำหรับการนำสายพันธุ์ต่างถิ่น การจัดสรรทรัพยากรไม่เพียงพอสำหรับหน่วยงานอนุรักษ์และการจัดการอุทยาน การมีอยู่ของผู้อพยพผิดกฎหมายจำนวนมาก การเติบโตอย่างรวดเร็วของการท่องเที่ยวที่ไม่สามารถควบคุมได้ การประมงเกินความสามารถ และการตกปลาเพื่อกีฬา | [72][73] [74][75] |
| เขตรักษาพันธุ์สัตว์ป่ามานสะ | รัฐอัสสัม, 26°30′N 91°51′E / 26.500°N 91.850°E |
ธรรมชาติ: (vii), (ix), (x) |
39,100 (97,000) | 1985 | 1992–2011 | การลักลอบล่าสัตว์ ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของอุทยาน และจำนวนประชากรบางชนิดลดลง โดยเฉพาะแรดหงอนใหญ่ หลังจากการรุกรานโดยกลุ่มติดอาวุธของ ชนเผ่าโบโด ในปี 1992 | [76][77] [78] | |
| ป้อมและสวนชาลามาร์ในลาฮอร์ | 
|
แคว้นปัญจาบ, 31°35′25″N 74°18′35″E / 31.59028°N 74.30972°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (i), (ii), (iii) |
— | 1981 | 2000–2012 | การทำลายแท้งค์เก็บน้ำประวัติศาสตร์ในปี 1999 เพื่อขยายถนนและกำแพงโดยรอบของสวนที่ทรุดโทรม ขึ้นบัญชีแหล่งมรดกโลกในภาวะอันตรายตามคำขอของรัฐบาลปากีสถาน | [79][80] |
| นาขั้นบันไดแห่งกลุ่มทิวเขาฟิลิปปินส์ | 
|
จังหวัดอีฟูเกา, 16°55′N 121°3′E / 16.917°N 121.050°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (iii), (iv), (v) |
500,000 (1,200,000) | 1995 | 2001–2012 | ขาดการติดตามอย่างเป็นระบบหรือแผนการจัดการที่ครอบคลุม | [81][82] |
| แบมและภูมิทัศน์วัฒนธรรม | 
|
จังหวัดเคร์มอน, 29°07′01″N 58°22′07″E / 29.11694°N 58.36861°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (ii), (iii), (iv), (v) |
— | 2004 | 2004–2013 | หลังได้รับความเสียหายจากแผ่นดินไหวในปี 2546 | [83][84][85] |
| ซากโบราณสถานกิลวากีซีวานีและซากโบราณสถานซองโกอึมนารา | Kilwa District, 8°57′28″S 39°31′22″E / 8.95778°S 39.52278°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (iii) |
— | 1981 | 2004–2014 | การเสื่อมสภาพอย่างต่อเนื่องของพื้นที่เนื่องจากปัจจัยต่าง ๆ เช่น การกัดเซาะหรือพืช | [86][87] | |
| อุทยานแห่งชาติโลสกาติโอส | 
|
จังหวัดอันติโอเกียและโชโก, 7°40′0″N 77°0′0″W / 7.66667°N 77.00000°W |
ธรรมชาติ: (ix), (x) |
72,000 (180,000) | 1994 | 2009–2015 | การตัดไม้ทำลายป่า การทำประมง และการล่าสัตว์อย่างผิดกฎหมาย | [88] |
| โบราณสถานแห่งมสเคทา | 
|
Mtskheta-Mtianeti, 41°50′32″N 44°43′16″E / 41.84222°N 44.72111°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (iii), (iv) |
— | 1994 | 2009–2016 | การเสื่อมสภาพของงานหินและจิตรกรรมฝาผนัง การจัดการที่ไม่ถูกต้อง และการพัฒนาเมือง | [89][90] |
| อาสนวิหารบากรัตและอารามเกลาที | 
|
จังหวัดอีเมเรตี, 42°15′44″N 42°42′59″E / 42.26222°N 42.71639°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (iv) |
7.87 (19.4) | 1994 | 2010–2017 | โครงการปรับปรุงครั้งใหญ่ที่จะนำไปสู่การแทรกแซงที่ไม่สามารถย้อนกลับได้ ขอบเขตของแหล่งมรดกโลกได้รับการแก้ไขในปี 2560[nb 2] อาสนวิหารบากราตีถูกถอดออกจากบัญชีมรดกโลกหลังจากการบูรณะใหม่ อย่างไรก็ตามอารามเกลาทียังอยู่ในบัญชี | [91][92][93] |
| อุทยานแห่งชาติกอมอเอ | 
|
Zanzan, 9°10′N 3°40′W / 9.167°N 3.667°W |
ธรรมชาติ: (ix), (x) |
1,150,000 (2,800,000) | 1983 | 2003–2017 | ความไม่สงบ การลักลอบล่าสัตว์ และการขาดกลไกการจัดการที่มีประสิทธิภาพ | [94][95] |
| อุทยานแห่งชาติซีเมียน | 
|
เขตอามารา, 13°11′N 38°4′E / 13.183°N 38.067°E |
ธรรมชาติ: (vii), (x) |
22,000 (54,000) | 1978 | 1996–2017 | ความลดจำนวนประชากร Walia ibex | [96][97] |
| ระบบอนุรักษ์เทือกปะการังเบลีซ | 
|
Belize, Stann Creek and Toledo 17°19′N 87°32′W / 17.317°N 87.533°W |
ธรรมชาติ: (vii), (ix), (x) |
96,300 (238,000) | 1996 | 2009–2018 | การทำลายป่าชายเลนและการพัฒนามากเกินไป | [98][99][100] |
| สถานที่ประสูติของพระเยซู : โบสถ์พระคริสตสมภพและเส้นทางการจาริกแสวงบุญ เบธเลเฮม | 
|
เบธเลเฮม, 31°42′16″N 35°12′27″E / 31.70444°N 35.20750°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (iv), (vi) |
2.98 (7.4) | 2012 | 2012–2019 | ความเสียหายจากน้ำรั่ว | [101][102][103] |
| แหล่งผลิตดินประสิวฮัมเบอร์สโตนและซานตาเลารา | 
|
Tarapacá, 20°12′30″S 69°47′40″W / 20.20833°S 69.79444°W |
วัฒนธรรม: (ii), (iii), (iv) |
— | 2005 | 2005–2019 | ลักษณะโครงสร้างที่เปราะบางเนื่องจากขาดการบำรุงรักษาเป็นเวลา 40 ปี ที่สร้างความเสียหาย การก่อกวน และการรื้อถอนบางส่วน การปล้นสะดม | [104][105][106] |
| ลิเวอร์พูล เมืองการค้าทางทะเล | ลิเวอร์พูล อิงแลนด์, 53°24′24″N 2°50′40″W / 53.40667°N 2.84444°W |
วัฒนธรรม: (ii), (iii), (iv) |
136 (340) | 2004 | 2012–2021 | เนื่องจากมีข้อเสนอให้ปรับปรุงท่าเรือประวัติศาสตร์ภายใต้โครงการ Liverpool Waters (รวมถึงสนามกีฬา Bramley-Moore Dock ของ Everton F.C.); ถูกเพิกถอนจากบัญชีมรดกโลกในเดือนกรกฎาคม พ.ศ. 2564[107] | [108][109] | |
| อุทยานแห่งชาติซาลงกา | 
|
จังหวัดเอกาเตอร์ and จังหวัดบันดุนดู, 2°S 21°E / 2°S 21°E |
ธรรมชาติ: (vii), (ix) |
3,600,000 (8,900,000) | 1984 | 1999–2021 | การรุกล้ำและการก่อสร้างที่อยู่อาศัย ลบออกจากรายการสภาวะในอันตรายเนื่องจากมีการปรับปรุงสถานะการอนุรักษ์ | [110][111] [14][112] |
| หลุมฝังพระศพกษัตริย์ราชวงศ์บูกันดาที่กาซูบี | 
|
Kampala District, 0°19′45″N 32°33′12″E / 0.32917°N 32.55333°E |
วัฒนธรรม: (i), (iii), (iv), (vi) |
27 (67) | 2001 | 2010–2023 | เหตุเพลิงไหม้ในเดือนมีนาคม 2010 | [113][114] |
| อุทยานแห่งชาตินีโอโคโล-โคบา | 
|
13°0′N 12°40′W / 13.000°N 12.667°W |
ธรรมชาติ: (x) |
913,000 (2,260,000) | 1981 | 2007–2024 | ความเสื่อมโทรมของทรัพย์สิน จำนวนสัตว์เลี้ยงลูกด้วยนมน้อย ปัญหาการจัดการ และผลกระทบของโครงการเขื่อนบนแม่น้ำแกมเบีย | [115] |
หมายเหตุ
[แก้]
อ้างอิงผิดพลาด: ป้ายระบุ
<ref> ชื่อ "status" ซึ่งนิยามใน <references> ไม่ถูกใช้ในข้อความก่อนหน้าอ้างอิง
[แก้]- อ้างอิง
- ↑ "List of World Heritage in Danger". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 10 July 2019.
- ↑ "World Heritage List Statistics". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 10 July 2019.
- ↑ "World Heritage Committee: Eighth session" (PDF). UNESCO. p. 18. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "Ngorongoro Conservation Area". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "World Heritage Committee: Thirteenth session" (PDF). UNESCO. p. 14. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "Plitvice Lakes National Park". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 16th session 1992, pp. 24–25
- ↑ 21st session 1997, pp. 10–11
- ↑ "Dubrovnik". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "World Heritage Committee: Fifteenth session" (PDF). UNESCO. p. 31. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "World Heritage Committee: Twenty-second session" (PDF). UNESCO. pp. 12–13. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "Wieliczka Salt Mine". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "World Heritage Committee: Twenty-second session" (PDF). UNESCO. p. 13. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 23rd session 1999, p. 29
- ↑ "Iguaçu National Park". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 25th session 2001, pp. 15–16
- ↑ "ธรรมชาติ and Culturo-Historical Region of Kotor". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "World Heritage Committee: Third session" (PDF). UNESCO. p. 13. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 27th session 2003, p. 27
- ↑ "Yellowstone National Park". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "World Heritage Committee: Nineteenth session" (PDF). UNESCO. pp. 18–19. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 16th session 1992, pp. 16–17
- ↑ "Srebarna Nature Reserve". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 16th session 1992, pp. 21–22
- ↑ 27th session 2003, p. 15
- ↑ "Angkor". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 28 May 2010.
- ↑ 16th session 1992, pp. 37–38, annex VI
- ↑ 28th session 2004, pp. 66–67
- ↑ "Bahla Fort". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2010.
- ↑ "World Heritage Committee: Twelfth session" (PDF). UNESCO. p. 19. สืบค้นเมื่อ 28 May 2010.
- ↑ 28th session 2004, p. 64
- ↑ "World Heritage Committee: Eleventh session" (PDF). UNESCO. p. 7. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิม (PDF)เมื่อ 5 February 2012. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "Rwenzori Mountains National Park". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 28th session 2004, p. 55
- ↑ "Butrint". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2010.
- ↑ 21st session 1997, pp. 24–25
- ↑ 29th session 2005, pp. 31–32
- ↑ "Timbuktu". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "World Heritage Committee: Fourteenth session" (PDF). UNESCO. p. 8. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 29th session 2005, pp. 20–21
- ↑ "Sangay National Park". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 16th session 1992, pp. 25–26
- ↑ 29th session 2005, pp. 18–19
- ↑ "Cologne Cathedral". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 28th session 2004, p. 116
- ↑ 30th session 2006, p. 46
- ↑ 8th session 1984, p. 18
- ↑ "Djoudj National Bird Sanctuary". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "World Heritage Committee: Twelfth session" (PDF). UNESCO. pp. 7, 16. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 24th session 2000, pp. 109–110
- ↑ 29th session 2005, pp. 15–16
- ↑ 30th session 2006, pp. 23–24
- ↑ "Group of Monuments at Hampi". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 23rd session 1999, pp. 32–33
- ↑ 30th session 2006, pp. 38–40
- ↑ "Ichkeul National Park". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 20th session 1996, pp. 31–32
- ↑ 30th session 2006, pp. 25–26
- ↑ "Tipasa". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "World Heritage Committee: Twenty-sixth session" (PDF). UNESCO. pp. 36–37. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 30th session 2006, p. 32
- ↑ "Kathmandu Valley". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 27th session 2003, pp. 64–65
- ↑ 31st session 2007, p. 32
- ↑ "Royal Palaces of Abomey". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "Royal Palaces of Abomey: Advisory Body Evaluation" (PDF). UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ "World Heritage Committee: Ninth session" (PDF). UNESCO. p. 7. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิม (PDF)เมื่อ 20 กันยายน 2011. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 กรกฎาคม 2011.
- ↑ 31st session 2007, pp. 21–22
- ↑ "Dresden Elbe Valley". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 30th session 2006, pp. 112–113
- ↑ "World Heritage Committee removes Baku from Danger List welcoming improvements in the ancient city's preservation". UNESCO. 25 June 2009. สืบค้นเมื่อ 21 June 2016.
- ↑ "Galápagos Islands". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- ↑ 30th session 2006, pp. 70–71
- ↑ 31st session 2007, pp. 68–69
- ↑ 34th session 2010, pp. 34–35
- ↑ "Manas Wildlife Sanctuary". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 28 May 2010.
- ↑ 16th session 1992, p. 28
- ↑ "Successful preservation of India's Manas Wildlife Sanctuary enables withdrawal from the List of World Heritage in Danger". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 28 May 2010.
- ↑ "Fort and Shalamar Gardens in Lahore". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 28 May 2010.
- ↑ 24th session 2000, p. 26
- ↑ "Rice Terraces of the Philippine Cordilleras". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 28 June 2012.
- ↑ 25th session 2001, pp. 139–141
- ↑ "Bam and its วัฒนธรรม Landscape". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 December 2010.
- ↑ 28th session 2004, pp. 47–48
- ↑ "World Heritage Committee removes the Iranian World Heritage site of Bam and its วัฒนธรรม Landscape from danger listing". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 13 July 2013.
- ↑ "Ruins of Kilwa Kisiwani and Ruins of Songo Mnara". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 28 May 2010.
- ↑ 28th session 2004, pp. 96–97
- ↑ "Colombia's Los Katíos National Park removed from List of Heritage in Danger". World Heritage Committee. UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 15 July 2015.
- ↑ "Historical Monuments of Mtskheta". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 December 2010.
- ↑ 33rd session 2009, p. 139
- ↑ "Bagrati Cathedral and Gelati Monastery". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 December 2010.
- ↑ 34th session 2010, pp. 130–133
- ↑ "Gelati Monastery, Georgia, removed from UNESCO's List of World Heritage in Danger". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 13 July 2017.
- ↑ "Comoé National Park". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 28 May 2010.
- ↑ 27th session 2003, p. 30
- ↑ "Simien National Park". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 1 August 2010.
- ↑ 20th session 1996, pp. 28–29
- ↑ "Belize Barrier Reef Reserve System". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 28 May 2010.
- ↑ 33rd session 2009, pp. 81–82
- ↑ "Belize Barrier Reef Reserve System removed from the List of World Heritage in Danger". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 27 June 2018.
- ↑ "Birthplace of Jesus: Church of the Nativity and the Pilgrimage Route, Bethlehem". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 30 June 2012.
- ↑ "Church of the Nativity and the Pilgrimage Route in Bethlehem, Palestine, inscribed on UNESCO World Heritage List along with sites from Israel, Palau, Indonesia and Morocco". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 30 June 2012.
- ↑ "The site of the Birthplace of Jesus in Bethlehem (Palestine) removed from the List of World Heritage in Danger". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 7 July 2019.
- ↑ "Humberstone and Santa Laura Saltpeter Works". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 28 May 2010.
- ↑ 29th session 2005, pp. 142–143
- ↑ "The Humberstone and Santa Laura Saltpeter Works site (Chile), removed from the List of World Heritage in Danger". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 7 July 2019.
- ↑ "Liverpool stripped of Unesco World Heritage status". BBC News (ภาษาอังกฤษแบบบริติช). 2021-07-21. สืบค้นเมื่อ 2021-07-21.
- ↑ "Liverpool – Maritime Mercantile City". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 27 October 2012.
- ↑ "World Heritage Committee places Liverpool on List of World Heritage in Danger". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 27 October 2012.
- ↑ "Salonga National Park". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 28 May 2010.
- ↑ 8th session 1984, p. 14
- ↑ "Salonga National Park (Democratic Republic of the Congo) removed from the List of World Heritage in Danger". 19 July 2021.
- ↑ "Tombs of Buganda Kings at Kasubi". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 28 May 2010.
- ↑ 34th session 2010, pp. 103–105
- ↑ "Niokolo-Koba National Park". UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 27 July 2024.
- ทั่วไป
- "World Heritage in Danger: A compendium of key decisions on the conservation of natural World Heritage properties via the List of World Heritage in Danger" (PDF). Gland, Switzerland: IUCN. 2009. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิม (PDF)เมื่อ 2010-12-30. สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 September 2011.
- Chape, Stuart; Spalding, Mark; Jenkins, Martin (2008). The world's protected areas: status, values and prospects in the 21st century (illustrated ed.). University of Castile-La Mancha. ISBN 978-0-520-24660-7. สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 September 2011.
- Timothy, Dallen J.; Nyaupane, Gyan P. (2009). Cultural heritage and tourism in the developing world: a regional perspective. Contemporary geographies of leisure, tourism and mobility. Vol. 10 (illustrated ed.). Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-415-77622-6. สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 September 2011.
- "World Heritage Committee: Eighth session" (PDF). UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- "World Heritage Committee: Sixteenth session" (PDF). UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 28 May 2010.
- "World Heritage Committee: Twentieth session" (PDF). UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- "World Heritage Committee: Twenty-first session" (PDF). UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 28 May 2010.
- "World Heritage Committee: Twenty-third session" (PDF). UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- "World Heritage Committee: Twenty-fourth session" (PDF). UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- "World Heritage Committee: Twenty-fifth session" (PDF). UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- "World Heritage Committee: Twenty-seventh session" (PDF). UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- "World Heritage Committee: Twenty-eighth session" (PDF). UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- "World Heritage Committee: Twenty-ninth session" (PDF). UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- "World Heritage Committee: Thirtieth session" (PDF). UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- "World Heritage Committee: Thirty-first session" (PDF). UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- "World Heritage Committee: Thirty-third session" (PDF). UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
- "World Heritage Committee: Thirty-fourth session" (PDF). UNESCO. สืบค้นเมื่อ 26 June 2011.
แหล่งข้อมูลอื่น
[แก้]- แหล่งมรดกโลก องค์การยูเนสโก - เว็บไซต์อย่างเป็นทางการ
- แหล่งมรดกโลกที่กำลังตกอยู่ในภาวะอันตราย องค์การยูเนสโก - เว็บไซต์อย่างเป็นทางการ
- ศูนย์มรดกยูเนสโก – รายชื่อมรดกโลก, เว็บไซต์อย่างเป็นทางการ







