ภาษาคอร์นวอลล์
| ภาษาคอร์นวอลล์ | |
|---|---|
| Kernewek, Kernowek | |
| ออกเสียง | แม่แบบ:IPA-kw |
| ประเทศที่มีการพูด | สหราชอาณาจักร |
| ภูมิภาค | คอร์นวอลล์ |
| ชาติพันธุ์ | ชาวคอร์นวอลล์ |
| สูญแล้ว | ปลายคริสต์ศตวรรษที่ 18[1][2][3][4] |
| ตระกูลภาษา | อินโด-ยูโรเปียน
|
| รูปแบบมาตรฐาน | รูปแบบการเขียนมาตรฐาน |
| ระบบการเขียน | ชุดตัวอักษรละติน |
| สถานภาพทางการ | |
| ภาษาชนกลุ่มน้อยที่รับรองใน | ประเทศอังกฤษ |
| ผู้วางระเบียบ | กลุ่มความร่วมมือภาษาคอร์นวอลล์ |
| รหัสภาษา | |
| ISO 639-1 | kw |
| ISO 639-2 | cor |
| ISO 639-3 | มีหลากหลาย:cor – คอร์นวอลล์สมัยใหม่cnx – คอร์นวอลล์สมัยกลางoco – คอร์นวอลล์เก่า |
| นักภาษาศาสตร์ | cnx คอร์นวอลล์สมัยกลาง |
| oco คอร์นวอลล์เก่า | |
| Linguasphere | 50-ABB-a |
 | |
ภาษาคอร์นวอลล์ (คอร์นวอลล์: Kernewek หรือ Kernowek;[6] แม่แบบ:IPA-kw; อังกฤษ: Cornish) เป็นภาษากลุ่มบริตันตะวันตกเฉียงใต้ในกลุ่มภาษาเคลต์ ถือเป็นภาษาฟื้นฟูหลังสูญเสียสถานะภาษาชุมชนที่ดำรงอยู่ในคอร์นวอลล์เมื่อปลายคริสต์ศตวรรษที่ 18 อย่างไรก็ตาม ความรู้ของภาษาคอร์นวอลล์ ซึ่งรวมถึงความสามารถในการพูดในระดับหนึ่ง ยังคงสืบทอดกันในครอบครัวและตัวบุคคล[7] และเริ่มต้นการฟื้นฟูในช่วงต้นคริสต์ศตวรรษที่ 20 มีผุ้พูดภาษานี้เป็นภาษาที่สองเพิ่มขึ้นต่อเนื่อง[8] และมีครอบครัวจำนวนน้อยมากที่เลี้ยงลูกให้พูดภาษาคอร์นวอลล์ฟื้นฟูเป็นภาษาแม่[9][10] ภาษาคอร์นวอลล์ได้รับการรับรองภายใต้กฎบัตรยุโรปของภาษาชนกลุ่มน้อยหรือภาษาท้องถิ่น (European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages)[11] และภาษานี้มักได้รับการระบุเป็นส่วนสำคัญของอัตลักษณ์ วัฒนธรรม และมรดกคอร์นวอลล์[12][13]
ภาษาคอร์นวอลล์ ภาษาเวลส์ และภาษาเบรอตาญ มีต้นตอจากภาษาบริตันทั่วไปที่เคยมีผุ้พูดทั่วบริเตนใหญ่ก่อนที่ภาษาอังกฤษจะเข้ามาแทนที่ ภาษานี้เคยเป็นภาษาหลักของคอร์นวอลล์ก่อนที่ภาษาอังกฤษดันภาษานี้ไปทางตะวันตก โดยมีความใกล้ชิดกับภาษาเบรอตาญ ซึ่งเป็นภาษาที่เข้าใจร่วมกัน หรือบางทีก็ตราบเท่าที่ภาษาคอร์นวอลล์ยังคงมีผุ้พูดเป็นภาษาถิ่นต่อไป[14][15] ภาษาคอร์นวอลล์ยังคงเป็นภาษาชุมชนทั่วไปในคอร์นวอลล์บางส่วนจนกระทั่งกลางคริสต์ศตวรรษที่ 18 มีหลักฐานความรู้ด้านภาษาบางส่วนที่ยังคงมีอยู่ในคริสต์ศตวรรษที่ 19 ซึ่งอาจเกือบซ้อนทับกับจุดเริ่มต้นการพยายามฟื้นฟูภาษานี้[16]
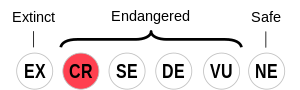
กระบวนการฟื้นฟูภาษานี้เริ่มขึ้นในช่วงต้นคริสต์ศตวรรษที่ 20 และใน ค.ศ. 2010 ทางยูเนสโกประกาศว่า สถานะเก่าของภาษาในฐานะ "ภาษาสูญแล้ว" นั้น "ไม่ถูกต้องอีกต่อไป"[17] นับตั้งแต่การฟื้นฟูภาษา เริ่มมีการตีพิมพ์หนังสือเรียนและผลงานวรรณกรรมคอร์นวอลล์บางส่วน และมีผู้เรียนภาษานี้เพิ่มขึ้น[8] การพัฒนาในช่วงล่าสุด ได้แก่ ดนตรีคอร์นวอลล์[18] ภาพยนตร์อิสระ[19] และหนังสือสำหรับเด็ก ประชากรจำนวนน้อยในคอร์นวอลล์ได้รับการเลี้ยงดูให้พูดได้สองภาษา[20][21] มีการสอนภาษานี้ในโรงเรียน และปรากฏบนป้ายจราจร[22][23]
สถานะทางกฎหมายและการรับรอง
[แก้]ใน ค.ศ. 2002 รัฐบาลสหราชอาณาจักรรับรองภาษาคอร์นวอลล์ภายใต้กฎบัตรยุโรปของภาษาชนกลุ่มน้อยหรือภาษาท้องถิ่นส่วนที่ 2[24] แผนที่ชุดภาษาใกล้สูญของโลกของยูเนสโกจัดให้ภาษานี้อยู่ในหมวด "ใกล้สูญขั้นวิกฤต" โดยทางยูเนสโกระบุว่า การจัดสถานะ 'สูญแล้ว' ครั้งก่อน "ไม่สะท้อนถึงสถานะปัจจุบันของภาษาคอร์นวอลล์" และ "ไม่ถูกต้องอีกต่อไป"[17]
ในสหราชอาณาจักร
[แก้]นโยบายของสภาคร์นวอลล์คือสนับสนุนภาษานี้ตามกฎบัตรยุโรป โดยสภาผ่านญัตติในเดือนพฤศจิกายน ค.ศ. 2009 ที่ส่งเสริมให้รวมภาษาคอร์นวอลล์ไว้ในสิ่งพิมพ์ของสภาและบนป้าย ตามความเหมาะสมและเท่าที่เป็นไปได้[25] แผนนี้ก่อให้เกิดเสียงวิจารณ์บางส่วน[26] ในเดือนตุลาคม ค.ศ. 2015 สภาคอร์นวอลล์ประกาศให้บุคลากรสนับสนุนให้ใช้ "คำและวลีพื้นฐาน" ในภาษาคอร์นวอลล์เมื่อต้องติดต่อกับสาธารณะ[27]
ใน ค.ศ. 2014 รัฐบาลสหราชอาณาจักรรรับรองชาวคอร์นวอลล์เป็นชนกลุ่มน้อยแห่งชาติตามกรอบอนุสัญญาว่าด้วยการคุ้มครองชนกลุ่มน้อยแห่งชาติ (Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities; FCNM)[28]
ใน ค.ศ. 2016 รัฐบาลบริติชยกเลิกการให้เงินทุนสำหรับภาษาคอร์นวอลล์ และถ่ายโอนความรับผิดชอบไปยังสภาคอร์นวอลล์[29]
ตัวอย่าง
[แก้]จากปฏิญญาสากลว่าด้วยสิทธิมนุษยชน:
| คอร์นวอลล์ | แปลไทย |
|---|---|
| y gila yn spyrys a vrederedh. | ด้วยจิตวิญญาณแห่งภราดรภาพ |
อ้างอิง
[แก้]- ↑ Spriggs, Matthew. "Where Cornish was Spoken and When: A Provisional Synthesis" (ภาษาอังกฤษ). เก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ Apr 26, 2023.
- ↑ Ó Riagáin, Dónall (13 January 2015). "Cracks in the foundation of a language empire – the resurgence of autochthonous lesser used languages in the United Kingdom and Northern Ireland". ใน Stolz, Christel (บ.ก.). Language Empires in Comparative Perspective (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Berlin, München, Boston: De Gruyter. pp. 77–88. doi:10.1515/9783110408362.77. ISBN 978-3-11-040836-2. สืบค้นเมื่อ 11 September 2021.
- ↑ MacAulay, Donald (1992). The Celtic languages. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press. p. 346. ISBN 0-521-23127-2. OCLC 24541026.
- ↑ Ball, Martin (2009). The Celtic Languages (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Nicole Muller (2nd ed.). Hoboken: Taylor & Francis. p. 491. ISBN 978-0-203-88248-1. OCLC 438705548.
- ↑ Moseley, Christopher; Nicolas, Alexander, บ.ก. (2010). Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger (PDF) (3rd ed.). Paris: UNESCO. ISBN 978-92-3-104096-2. เก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 23 July 2022.
- ↑ "Gerlyver Kernewek" (ภาษาคอร์นิช). www.cornishdictionary.org.uk. สืบค้นเมื่อ 17 October 2019.
- ↑ Mackinnon, Ken. "Cornish at Its Millennium: An Independent Study of the Language". Cornish Studies (ภาษาอังกฤษ). 10.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 O'Neill, Diarmuid (2005). Rebuilding the Celtic Languages: Reversing Language Shift in the Celtic Countries (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Y Lolfa. p. 240. ISBN 0-86243-723-7.
- ↑ Linguistic minorities in countries belonging to the European community: summary report (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Commission of the European Communities. 1986. p. 195.
- ↑ Deacon, Bernard; Tregidga, Garry; Cole, Richard (2003). Mebyon Kernow and Cornish Nationalism (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Welsh Academic Press. pp. 132.
- ↑ "Cornish gains official recognition". BBC News (ภาษาอังกฤษ). 6 November 2002. สืบค้นเมื่อ 11 November 2012.
- ↑ "Funding boost to safeguard Cornish language announced". gov.uk (ภาษาอังกฤษ). 13 March 2015.
- ↑ "Kowethas an Yeth Kernewek wins Heritage Lottery Fund support" (ภาษาอังกฤษ). 19 August 2014. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 31 March 2016.
- ↑ Jackson, Kenneth Hurlstone (1953). Language and history in early Britain: a chronological survey of the Brittonic languages, 1st to 12th c. A.D. (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press. p. 12. ISBN 0-85224-116-X. OCLC 217631525.
- ↑ Pool, P. A. S. (1975). William Bodinar's letter, 1776 (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Journal of the. Royal Institution of Cornwall. OCLC 927038181.
[In 1746] Captain Samuel Barrington, in the course of naval duties, took a sailor from Mount's Bay who spoke Cornish well enough to make himself understood to Bretons
- ↑ Beresford Ellis, Peter (1990). The Story of the Cornish Language (ภาษาอังกฤษ). Tor Mark Press. pp. 19–25. ISBN 0-85025-371-3.
Of John Davey of Zenmor who died in 1891, it was claimed that he was the last surviving native speaker of the language. His stone memorial reads 'John Davey 1812-1891 of Boswednack in this parish ... who was the last to possess any traditional considerable knowledge of the Cornish Language.'
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "Cornish language no longer extinct, says UN". BBC News Online (ภาษาอังกฤษ). 7 December 2010. สืบค้นเมื่อ 11 November 2012.
- ↑ "Music". Cornish Language Partnership. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 25 December 2008.
- ↑ "Film clips: Here you can watch clips from films made in Cornish". Cornish Language Partnership. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 25 December 2008.
- ↑ MacKinnon, Ken. "Cornish Language Study 2000". Cornish Language Partnership (ภาษาอังกฤษ). คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 3 December 2013.
- ↑ Cornish ที่ Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (ต้องสมัครสมาชิก)
- ↑ "Cornish language – is it dead?". This is The West Country (ภาษาอังกฤษ). 21 February 2009. สืบค้นเมื่อ 11 November 2012.
- ↑ Greenaway, Aaron (22 August 2020). "The Cornish road signs that still point to a past that no longer exists". CornwallLive.
- ↑ Ball 2009, p. 769.
- ↑ Birch, Sophie (March 2010). "Cornwall cultural strategy evidence report" (PDF). Cornwall Council. p. 24. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิม (PDF)เมื่อ 2018-04-19. สืบค้นเมื่อ 19 April 2018.
- ↑ "Dyslexic councillor says Cornish language road signs could prove dangerous for drivers". Plymouth Herald. 21 July 2014. คลังข้อมูลเก่าเก็บจากแหล่งเดิมเมื่อ 29 July 2014. สืบค้นเมื่อ 29 July 2014.
- ↑ Elgot, Jessica (7 October 2015). "Cornwall council plans to encourage staff to speak Cornish". The Guardian.
- ↑ Milmo, Cahal (23 April 2014). "Cornish to be recognised as a national minority along with Scots, Welsh and Irish". The Independent. สืบค้นเมื่อ 3 February 2019.
- ↑ "Cornish language funding stopped by government". BBC News. 21 April 2016.
บรรณานุกรม
[แก้]- Bruch, Benjamin; Bock, Albert (2008) An Outline of the Standard Written Form of Cornish. Cornish Language Partnership
- Hodge, Pol (2001) Cornish Names. Truro: Dyllansow Fentenwynn ISBN 1 902917 23 5
- Jago, F. W. P., A Cornish Dictionary (1887) English Cornish dictionary
- Jenner, Henry, A handbook of the Cornish language : chiefly in its latest stages with some account of its history and literature (1904) [1] [2]
- Ellis, Peter B. (1971) The Story of the Cornish Language. 32 p. Truro: Tor Mark Press
- Ellis, Peter B. (1974) The Cornish Language and its Literature. ix, 230 p. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul
- Everson, Michael (2007) A Proposed Standard Written Form of Cornish. Cornish Language Partnership Process
- Ferdinand, Siarl (2013). Brief History of the Cornish language, its Revival and its Current Situation. E-Keltoi, Vol. 2, 2 Dec pp. 199–227 [3]
- Jackson, Kenneth (1953) Language and History in Early Britain: a chronological survey of the Brittonic languages, first to twelfth century a.D. Edinburgh: U. P. 2nd ed. Dublin : Four Courts Press, 1994 has a new introduction by William Gillies
- Norris, Edwin, Sketch of Cornish grammar (1859) [4] [5] [6]
- Sandercock, Graham (1996) A Very Brief History of the Cornish Language. Hayle: Kesva an Tavas Kernewek ISBN 0-907064-61-2
- Stokes, Whitley, Gwreans an bys = The Creation of the world : a Cornish mystery (1863)
- Weatherhill, Craig (1995) Cornish Place Names & Language. Wilmslow: Sigma Press (reissued in 1998, 2000 ISBN 1-85058-462-1; second revised edition 2007 ISBN 978-1-85058-837-5)
- Weatherhill, Craig (2009) Concise Dictionary of Cornish Place-names ; edited by Michael Everson. Westport, Co. Mayo: Evertype ISBN 978-1-904808-22-0
- Williams, G. P, The preverbal particle Re in Cornish (1908)
แหล่งข้อมูลอื่น
[แก้]- A Handbook of the Cornish Language, by Henry Jenner A Project Gutenberg eBook
- Cornish Language Partnership website
- Endangered Languages Project: Cornish
