ผู้ใช้:Subpadon/การสะท้อน (ฟิสิกส์)
รอการแปล

การสะท้อน (อังกฤษ: reflection)) หมายการเปลี่ยนแปลงทิศทางของหน้าคลื่นที่รอยต่อของตัวกลางสองชนิดและทำให้หน้าคลื่นหันกลับไปยังฝั่งของตัวกลางชนิดแรก ตัวอย่างเช่น การสะท้อนของแสง คลื่นน้ำ คลื่นเสียง โดยอยู่ภายใต้ กฎการสะท้อน ที่กล่าวว่า ที่พื้นผิวใดๆ มุมตกกระทบ (θi) จะมีค่าเท่ากับมุมสะท้อน (θr) ณ จุดที่เกิดการสะท้อนนั้น กระจกเงาเป็นตัวอย่างหนึ่งของการสะท้อนที่เป็นระเบียบของแสง
สำหรับการสะท้อนของคลื่นเสียงทำให้เกิดการกังวานของเสียง ซึ่งเป็นหลักการสำคัญที่ใช้ในระบบวิเคราะห์ตำแหน่งของวัตถุในลักษณะเดียวกับค้างคาว ในทางธรณีวิทยา การสะท้อนของคลื่นมีส่วนสำคัญในการศึกษาคลื่นไหวสะเทือน การสะท้อนของคลื่นยังสามารถพบเห็นได้ในคลื่นน้ำ คลื่นแม่เหล็กไฟฟ้า การสะท้อนมีความสำคัญในระบบโทรคมนาคม ติดต่อ สื่อสารผ่านคลื่นวิทยุ และสำหรับการสำรวจด้วยเรดาร์
การสะท้อนของแสง
[แก้]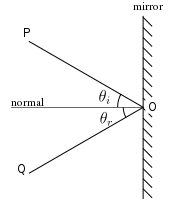
แสงอาจเกิดการสะท้อนสมบูรณ์ (specular reflection) เช่นการสะท้อนผ่านกระจกเงา หรือสะท้อนไม่สมบูรณ์ (diffuse reflection) ซึ่งสูญเสียภาพเชิงฟิสิกส์แต่อนุรักษ์พลังงาน ขึ้นกับชนิดของตัวกลางทึบแสงซึ่งแสงเกิดการสะท้อน
กระจกเงาเป็นตัวอย่างที่สำคัญในการสะท้อนที่สมบูรณ์ กระจกเงาประกอบด้วยแผ่นแก้วที่ฉาบด้วยโลหะ ที่พื้นผิวโลหะที่ฉาบบนแผ่นแก้วนี้เองที่เกิดการสะท้อนของแสง การสะท้อนของแสงยังอาจเกิดได้กับพื้นผิวประเภทโปร่งแสงเช่น การสะท้อนของแสงบนผิวน้ำ หรือกระจกใส
ในแผนภาพทางด้านซ้ายมือ รังสีตกกระทบ PO ตกสู่กระจกเงาที่จุด O และสะท้อนออกเกิดเป็นรังสีสะท้อน OQ เส้นตั้งฉากกับพื้นผิวสะท้อน (กระจกเงา) มีชื่อเรียกว่าเส้นปกติหรือเส้นตั้งฉาก มุมตกกระทบ 'θi คือมุมที่วัดจากรังสีตกกระทบสู่เส้นตั้งฉาก ในทำนองเดียวกันมุมสะท้อน 'θr คือมุมที่เกิดจากรังสีสะท้อนตัดกับเส้นตั้งฉาก
ในธรรมชาติ การสะท้อนของแสงเกิดขึ้นที่ทุกพื้นผิวสัมผัสระหว่างตัวกลางสองชนิดที่มีดัชนีการหักเหแสงที่แตกต่างกัน กล่าวคือ การสะท้อนของแสงผ่านกระจกเงาก็คือการสะท้อนของแสงที่ผิวสัมผัสระหว่างแก้วกับโลหะที่ฉาบไว้ ในขณะที่การสะท้อนบนผิวน้ำก็คือการสะท้อนที่เกิดขึ้นที่ผิวสัมผัสระหว่างน้ำกับอากาศ โดยทั่วไปแสงส่วนหนึ่งจะเกิดการสะท้อนที่ผิวสัมผัสของวัตถุดังกล่าวและส่วนที่เหลือจะหักเหและเดินทางเข้าสู่ตัวกลางชนิดที่สอง จากสมการของแมกซ์เวลล์ซึ่งใช้อธิบายการเดินทางของแสงที่ผิวสัมผัสของตัวกลาง เราสามารถพิสูจน์ต่อได้เป็นสมการของเฟรชเนลซึ่งใช้คำนวณสัดส่วนปริมาณของคลื่นแสงที่หักเหเข้าสู่ตัวกลางที่สองและปริมาณของคลื่นแสงที่สะท้อนกลับสู่ตัวกลางที่หนึ่ง การสะท้อนกลับหมดของแสงเกิดขึ้นเมื่อแสงเดินทางจากตัวกลางที่มีความหนาแน่นสูงไปสู่ตัวกลางที่มีความหนาแน่นต่ำกว่าโดยมีมุมตกกระทบมากกว่ามุมวิกฤติ
ภาพสะท้อนจากกระจกเงาหรือวัสดุผิวมันอื่นๆ เกิดจากการสะท้อนของแสง ณ ผิววัตถุเหล่านั้น ภาพที่ได้จะมีลักษณะกลับข้างซ้ายขวาหรือที่เรียกว่าปรัศวภาควิโลม นอกจากนี้การสะท้อนบนกระจกนูนจะทำให้เกิดภาพที่มีขนาดใหญ่ขึ้น ในขณะที่การสะท้อนบนกระจกเงาเว้าจะทำให้ภาพที่ได้มีขนาดเล็กกว่าวัตถุ โดยพื้นผิวของกระจกเว้าหรือกระจกนูนเหล่านี้จะมีลักษณะเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของทรงกลมหรือพาราโบลอยด์
กฎการสะท้อน
[แก้]
สำหรับวัสดุผิวเรียบ การสะท้อนของแสง (หรือคลื่นอื่น) เกิดขึ้นในลักษณะสมบูรณ์
- รังสีตกกระทบ รังสีสะท้อน และเส้นตั้งฉาก ล้วนอยู่ในแนวระนาบเดียวกัน
- มุมตกกระทบเท่ากับมุมสะท้อน
กลไกของการสะท้อน
[แก้]จากความรู้เกี่ยวกับทฤษฎีคลื่นแม่เหล็กไฟฟ้าคลาสสิก แสงถูกจัดให้เป็นคลื่นแม่เหล็กไฟฟ้าชนิดหนึ่งซึ่งสามารถอธิบายได้ด้วยสมการของแมกซ์เวลล์ ด้วยหลักการนี้สามารถอธิบายกลไกการสะท้อนของแสงได้ กล่าวคือ คลื่นแสงซึ่งตกกระทบลงบนผิวของวัตถุทำให้เกิดการสั่นสะเทือนและเกิดการโพลาไรซ์ในระดับอะตอม (หรือการสั่นของอิเล็กตรอนในกรณีของโลหะ) ซึ่งส่งผลให้อนุภาคเหล่านี้เกิดการแผ่คลื่นทุติยภูมิในทุกทิศทาง ซึ่งทำให้เกิดหลักการของออยเกนส์และเฟรชเนลซึ่งอธิบายว่าคลื่นทุติยภูมิเหล่านี้เองคือการสะท้อนแบบสมบูรณ์กลับสู่ตัวกลางที่หนึ่งและการหักเหเข้าสู่ตัวกลางที่สอง
ในกรณีของฉนวนไฟฟ้าเช่นแก้ว สนามไฟฟ้าจากคลื่นแสงที่เกิดปฏิสัมพันธ์กับอิเล็กตรอนในแก้ว อิเล็กตรอนที่สั่นเหล่านี้สร้างสนามไฟฟ้าขึ้นและกลายเป็นตัวส่งคลื่นแม่เหล็กไฟฟ้า การหักเหของแสงในแก้วที่สังเกตได้เป็นคลื่นลัพธ์ที่ได้จากการรวมคลื่นตกกระทบเข้ากับคลื่นที่ปล่อยออกมาจากการสั่นของอนุภาคของแก้วในทิศทางเดียวกันกับคลื่นตกกระทบ ในขณะที่คลื่นจากการสั่นของอนุภาคของแก้วในทิศตรงกันข้ามทำให้เกิดการสะท้อนที่สังเกตได้ การแผ่รังสีของอนุภาคของตัวกลางนี้เกิดขึ้นทั่วไปในแก้วแต่ผลลัพธ์ที่ได้เทียบเท่ากับการสะท้อน ณ พื้นผิวแต่เพียงอย่างเดียว
ในปัจจุบัน แสงถูกอธิบายด้วยหลักการของควอนตัม ซึ่งพิจารณาแสงที่สามารถอยู่ในรูปของอนุภาค ริชาร์ด เฟยน์แมนได้อธิบายรายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับการสะท้อนของแสงไว้อย่างน่าสนใจในหนังสือ QED: The Strange Theory of Light and Matter
Other types of reflection
[แก้]Diffuse reflection
[แก้]
When light strikes the surface of a (non-metallic) material it bounces off in all directions due to multiple reflections by the microscopic irregularities inside the material (e.g. the grain boundaries of a polycrystalline material, or the cell or fiber boundaries of an organic material) and by its surface, if it is rough. Thus, an 'image' is not formed. This is called diffuse reflection. The exact form of the reflection depends on the structure of the material. One common model for diffuse reflection is Lambertian reflectance, in which the light is reflected with equal luminance (in photometry) or radiance (in radiometry) in all directions, as defined by Lambert's cosine law.
The light sent to our eyes by most of the objects we see is due to diffuse reflection from their surface, so that this is our primary mechanism of physical observation.[1]
Retroreflection
[แก้]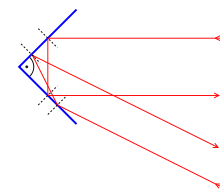
Some surfaces exhibit retroreflection. The structure of these surfaces is such that light is returned in the direction from which it came.
When flying over clouds illuminated by sunlight the region seen around the aircraft's shadow will appear brighter, and a similar effect may be seen from dew on grass. This partial retro-reflection is created by the refractive properties of the curved droplet's surface and reflective properties at the backside of the droplet.
Some animals' retinas act as retroreflectors, as this effectively improves the animals' night vision. Since the lenses of their eyes modify reciprocally the paths of the incoming and outgoing light the effect is that the eyes act as a strong retroreflector, sometimes seen at night when walking in wildlands with a flashlight.
A simple retroreflector can be made by placing three ordinary mirrors mutually perpendicular to one another (a corner reflector). The image produced is the inverse of one produced by a single mirror. A surface can be made partially retroreflective by depositing a layer of tiny refractive spheres on it or by creating small pyramid like structures. In both cases internal reflection causes the light to be reflected back to where it originated. This is used to make traffic signs and automobile license plates reflect light mostly back in the direction from which it came. In this application perfect retroreflection is not desired, since the light would then be directed back into the headlights of an oncoming car rather than to the driver's eyes.
Complex conjugate reflection
[แก้]Light bounces exactly back in the direction from which it came due to a nonlinear optical process. In this type of reflection, not only the direction of the light is reversed, but the actual wavefronts are reversed as well. A conjugate reflector can be used to remove aberrations from a beam by reflecting it and then passing the reflection through the aberrating optics a second time.
Neutron reflection
[แก้]Materials that reflect neutrons, for example beryllium, are used in nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons. In the physical and biological sciences, the reflection of neutrons off atoms within a material is commonly used to determine its internal structures.
Sound reflection
[แก้]When a longitudinal sound wave strikes a flat surface, sound is reflected in a coherent manner provided that the dimension of the reflective surface is large compared to the wavelength of the sound. Note that audible sound has a very wide frequency range (from 20 to about 17000 Hz), and thus a very wide range of wavelengths (from about 20 mm to 17 m). As a result, the overall nature of the reflection varies according to the texture and structure of the surface. For example, porous materials will absorb some energy, and rough materials (where rough is relative to the wavelength) tend to reflect in many directions—to scatter the energy, rather than to reflect it coherently. This leads into the field of architectural acoustics, because the nature of these reflections is critical to the auditory feel of a space. In the theory of exterior noise mitigation, reflective surface size mildly detracts from the concept of a noise barrier by reflecting some of the sound into the opposite direction.
Seismic reflection
[แก้]Seismic waves produced by earthquakes or other sources (such as explosions) may be reflected by layers within the Earth. Study of the deep reflections of waves generated by earthquakes has allowed seismologists to determine the layered structure of the Earth. Shallower reflections are used in reflection seismology to study the Earth's crust generally, and in particular to prospect for petroleum and natural gas deposits.
See also
[แก้]References
[แก้]- ↑ Mandelstam, L.I. (1926). "Light Scattering by Inhomogeneous Media". Zh. Russ. Fiz-Khim. Ova. 58: 381.
